IduwiniVoice Edubbas
Understanding the Technologies: Base Radios; What They Are And Their Safe Usage.

Base Radios: What They Are And Their Safe Usage.
In hazardous environments where safety is paramount, communication tools play a crucial role in ensuring the well-being of personnel. Tetra, VHF, UHF radios, and Compact Field Wireless (CFW) systems are technologies specifically designed to enable reliable communication in high-risk areas. In this article, we’ll delve into the features and applications of these communication tools, shedding light on how they contribute to enhanced safety in hazardous zones.
Understanding the Technologies
1. Tetra Radios:
Tetra (Terrestrial Trunked Radio) radios are digital two-way communication devices designed for mission-critical communications. They offer features such as group calling, emergency alerts, and encryption, making them ideal for hazardous areas. Tetra radios operate on a dedicated frequency band, ensuring interference-free communication.
2. VHF (Very High Frequency) Radios:
VHF radios operate on frequencies between 30 and 300 MHz. They provide good coverage over long distances and are often used in outdoor or open spaces. VHF radios are widely utilized in hazardous industries like mining and construction.
3. UHF (Ultra High Frequency) Radios:
UHF radios operate on frequencies between 300 MHz and 3 GHz. They are effective in providing communication within buildings, tunnels, and areas with obstacles that can interfere with signals. UHF radios are commonly used in industrial settings.
4. Compact Field Wireless (CFW) Systems:
CFW systems are advanced wireless solutions that enable seamless communication and data exchange in industrial environments. They are designed to withstand extreme conditions and can be integrated with sensors, enabling real-time monitoring of critical parameters.
Applications in Hazardous Areas
1. Tetra Radios:
Tetra radios find applications in oil and gas refineries, chemical plants, and mining sites. Their secure and reliable communication features are crucial for coordinating emergency responses, managing operations, and ensuring the safety of personnel.
2. VHF and UHF Radios:
VHF and UHF radios are used in a range of hazardous environments, including manufacturing facilities, construction sites, and offshore platforms. They enable clear communication over long distances and in areas with potential signal interference.
3. Compact Field Wireless (CFW) Systems:
CFW systems are utilized in various hazardous industries to monitor equipment conditions, track environmental factors, and ensure compliance with safety regulations. They provide real-time data to operators, helping them make informed decisions.
Benefits and Safety Considerations
Enhanced Communication: These technologies facilitate immediate communication, reducing response times during emergencies.
Durability: Designed to withstand harsh conditions, these tools are built for reliability in hazardous environments.
Monitoring Capabilities: CFW systems offer the advantage of continuous monitoring, enabling proactive maintenance and risk mitigation.
Intrinsically Safe Options: Many communication devices designed for hazardous areas adhere to intrinsically safe standards, reducing the risk of igniting flammable substances.
In hazardous areas, communication is not just about convenience; it’s a matter of safety and well-being. Tetra, VHF, UHF radios, and Compact Field Wireless (CFW) systems are essential tools that empower personnel to stay connected and informed, even in the most challenging environments. By leveraging these technologies, industries can uphold safety standards, respond effectively to emergencies, and ensure the protection of their most valuable asset—human lives.
IduwiniVoice Edubbas
‘Education Remain the Bedrock of Development’ — High Chief Angodideke

By: Derick Peretengboro
The growing belief that education remains a vital catalyst for development has been exemplified once again in the riverine Delta as the launch of the 2026 edition of the famous ‘Back to School’ initiative came alove in Delta State, courtesy of the Common Men Assembly (CMA). The body has reiterated its belief in education as a catalyst for development riverine Ijaw communities.
The programme, which focuses on supplying essential learning materials to public primary schools, is expected to benefit pupils in 25 communities across five local government areas.
Hight Chief Angodideke Jude, the Ogungbeiwei of Ngbilebiri-Mein Kingdom and Chairman of the CMA, while addressing stakeholders at the launch, said the initiative was conceived to address the persistent lack of basic educational infrastructure in riverine communities.
Working alongside Tantita Security Services Nigeria Limited and the Godfrey Pondi Book Club, the group distributed desks, books, bags, and sandals to selected schools on day one.
Schools in Okosugbene, Orugbene, and Ofogbene received 30 desks each, while other schools in Burutu and Warri South West LGAs received assorted learning materials.
The items were received by school officials and community leaders, including Mrs. Ebiyerin Esiri, Mr. Roland Government, and Mr. Oweikeniafa Ebi.
Pupils were seen excitedly engaging with the new materials, a development observers say could positively influence learning outcomes in the affected schools.
IduwiniVoice Edubbas
Wonders as Woman Lived with Parasitic Twin Inside Her for Almost 50 Years before Discovery
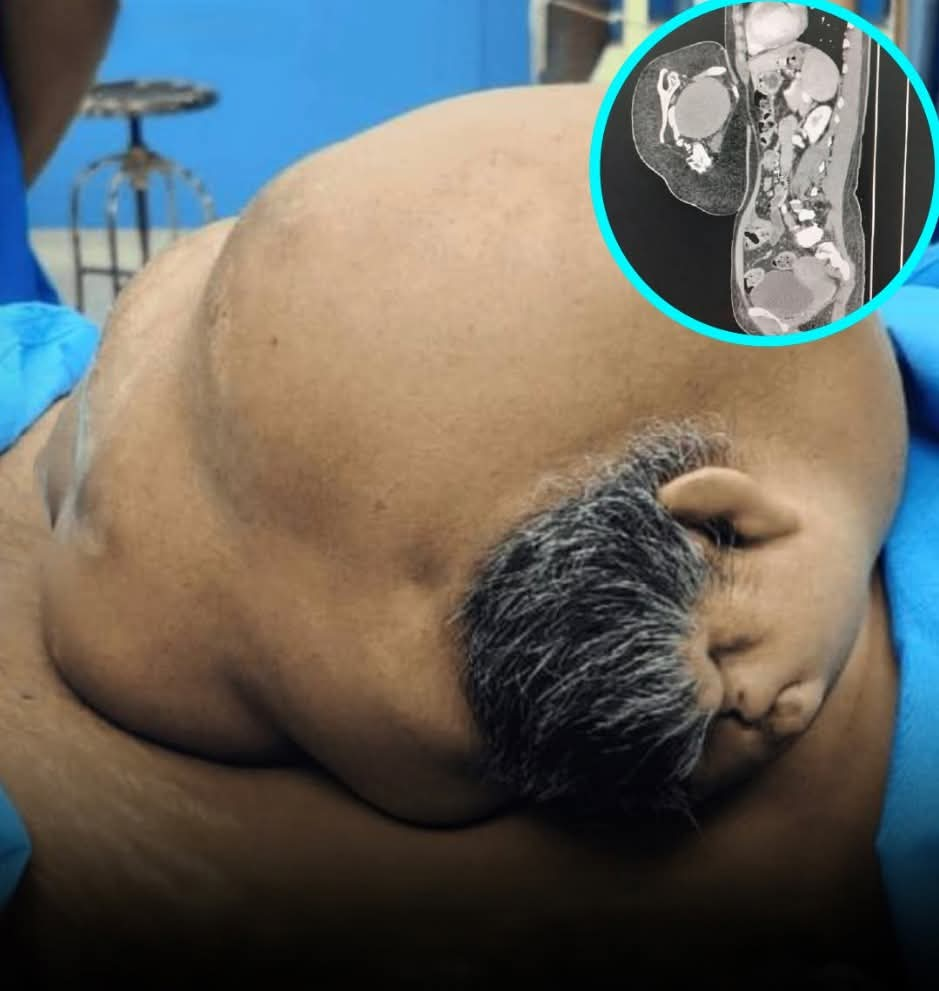
By: Daire Perez
Medical science isn’t just your everyday paracetamol and headache, seat back and be amazed by this rare and heartbreaking medical case. A 47-year-old woman recently learned that the large abdominal mass she had lived with since birth was in fact her undeveloped twin. The rare congenital condition known as an epigastric heteropagus twin, occurs when one embryo fails to fully develop and remains attached to the other during pregnancy.
According to reports, the woman – a mother of four – decided to undergo surgery after carrying the mass for nearly half a century. Surgeons discovered a 24-centimeter growth containing primitive human features, including an ear, a nose, and partially formed limbs. The mass was being nourished by an artery connected to the carrier’s abdomen.
Medical specialists involved in the case emphasized the crucial role of advanced imaging studies conducted before operation. These scans allowed doctors to precisely map the mass’s structure and safely remove it without endangering the patient’s life.
Cases of parasitic twins are extremely rare, making this one of the most unusual and fascinating occurrences in modern medical literature.
Adapted from Weired, Wonder, and Amazing Tings (Facebook)
IduwiniVoice Edubbas
TITANIC: A GRAVE IN THE DEEP – 113 YEARS LATER, QUESTIONS STILL HAUNT THE ATLANTIC

By Tama Peretengboro
Imagine the icy Atlantic, silent but for the fading cries of the doomed. On the early morning of April 15, 1912, the RMS Titanic-the so-called “unsinkable” ship-vanished beneath the surface of the North Atlantic,taking more than 1,500 lives with it.The tragedy remains one of the most devastating maritime disasters in history.
In the aftermath, survivors huddled in lifeboats, drifting in shock and silence.Many would later recall that the quiet that followed the sinking-the absence of voices, of splashes, of life – was more harrowing than the chaos itself.
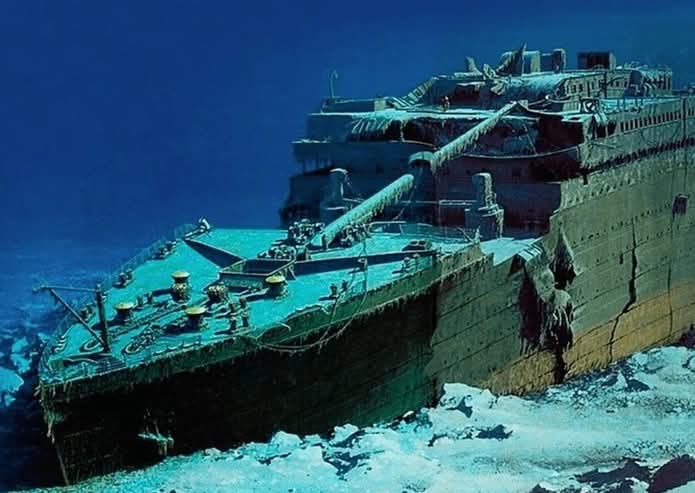
For over seven decades, the wreck lay undisturbed, lost to time and memory-untilb1985, when an expedition led by Dr. Robert Ballard discovered the remains of the Titanic nearly 2.5 miles beneath the surface.What they found was a ship torn apart-broken in two and scattered across the ocean floor like an open wound frozen in time.
Since then, more than 5,000 artifacts have been recovered from the site, each one a chilling reminder of that fateful night: bottles of perfume that still carry their scent, letters that never reached their destinations, pairs of shoes lying where their owners once stood. These personal items have become the voice of the dead,telling stories that words cannot.
But even as these objects are studied and displayed in exhibitions around the world, a haunting question remains: Are there human remains still at the site?
Marine scientists are divided. Some argue that the ocean’s immense pressure, low temperatures, and microbial activity would have long since broken down any human tissue. Others point to the way personal effects remain arranged-shoes placed side by side, clothing intact in some cases-suggesting bodies once rested there,perhaps shielded by the deep.
What’s clear is that the Titanic is more than a shipwreck. It is a sunken memorial, a timecapsule lying in darkness. Over a century later, it continues to stir emotion and inquiry, reminding us that beneath the waves lies a tragedy that time can not wash away.
Credit: Weired, Wonder, and Amazing Things on Facebook








